Shallow Proportions
Poor brilliance and light performance
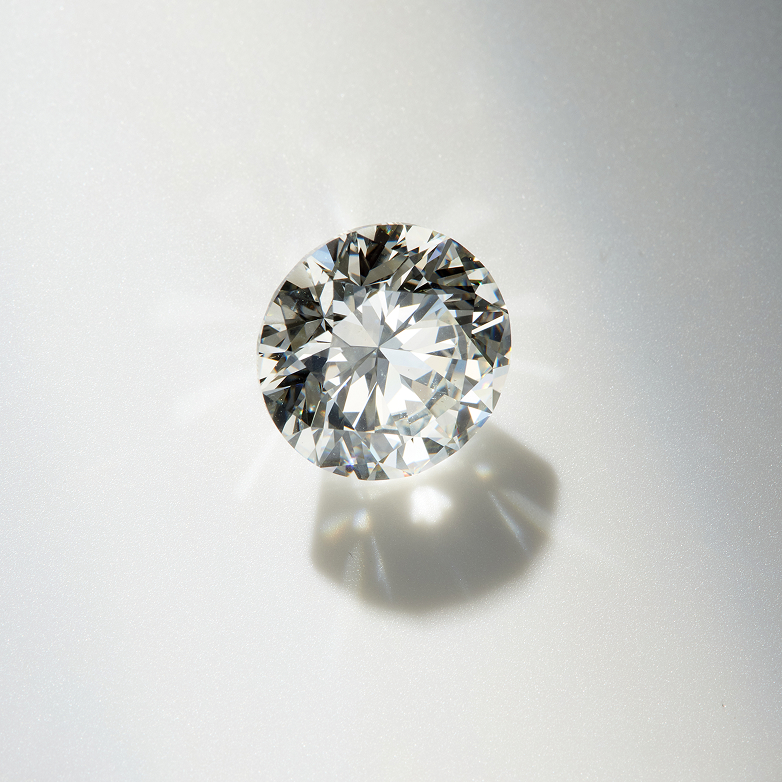

The diamond’s cut grade is one of the most important factors in determining a stone’s overall brilliance and beauty. Often mistaken for diamond shape, diamond cut grade actually refers to how well a diamond has been proportioned and faceted to maximize light reflection. Choosing an Excellent or Very Good cut grade ensures that your diamond captures and reflects light beautifully, creating that signature sparkle.
Simply put, a poorly cut diamond won’t shine as brightly—making cut grade a key detail you don’t want to overlook. When purchasing a diamond, always check its certification for the official cut grade and prioritize craftsmanship over size. A well-cut diamond will always outshine a poorly cut one.
Ahead, everything you need to know about diamond cut grade.
Diamond cut grade is one of the most critical factors in determining a diamond’s overall brilliance, fire, and scintillation—the way it reflects and disperses light. While often confused with diamond shape, cut grade actually refers to how well a diamond is proportioned and faceted to maximize light reflection. A poorly cut diamond, even with perfect clarity and color, can appear dull, while a well-cut diamond will sparkle beautifully.
The Gemological Institute of America (GIA) Cut Grading System, developed specifically for round brilliant diamonds, evaluates a diamond’s proportions, symmetry, and polish to determine how well it interacts with light. While fancy-shaped diamonds do not receive a formal cut grade, their facet alignment and proportioning still significantly impact their overall beauty.
To assess a diamond’s cut, GIA considers the following factors:
Proportions
The angles and relative measurements of a diamond’s facets, including depth, table size, crown angle, and pavilion depth. Well-proportioned diamonds optimize light return, enhancing sparkle.
Symmetry
The precision with which a diamond’s facets are aligned. Poor symmetry can create uneven light performance, diminishing brilliance.
Polish
The smoothness of a diamond’s surface, which affects how light enters and reflects within the stone. Poorly polished diamonds may scatter light, reducing their visual appeal.
Other Key Factors
Brightness (total light reflection), fire (dispersion of colored light), scintillation (flashes of sparkle when moved), weight ratio, and durability all contribute to a diamond’s cut quality.
Understanding these elements helps buyers choose a diamond that delivers exceptional light performance, ensuring it looks stunning in every setting.
Poor brilliance and light performance

Most brilliant. Optimal light performance

Poor brilliance and light performance
The table is the top horizontal facet of the diamond.
The crown height is the upper portion of the diamond.
The girdle is the middle portion of a diamond.
Pavilion angle is an important dimension of the stone
The small facet at the bottom of a diamond to prevent chipping and abrasion to the point.
The diamond’s overall depth from the surface of the table to the culet.
A poorly cut diamond that appears dull and lacks fire due to excessive light loss.
Still offers a decent amount of sparkle, but some light leakage occurs, reducing overall brightness.
Still offers a decent amount of sparkle, but some light leakage occurs, reducing overall brightness.
Nearly as brilliant as Excellent, with only slight differences in light performance that are difficult to detect.
The highest cut grade, offering maximum brilliance, fire, and scintillation. Light is reflected efficiently, creating the most dazzling effect.
The GIA Cut Grade Scale applies specifically to round brilliant diamonds and is divided into five categories, explained below.
Excellent: The highest cut grade, offering maximum brilliance, fire, and scintillation. Light is reflected efficiently, creating the most dazzling effect.
Very Good: Nearly as brilliant as Excellent, with only slight differences in light performance that are difficult to detect.
Good: Still offers a decent amount of sparkle, but some light leakage occurs, reducing overall brightness.
Fair: Displays noticeable light leakage, resulting in a lack of brilliance and sparkle.
Poor: A poorly cut diamond that appears dull and lacks fire due to excessive light loss.
When shopping for a diamond, cut grade should be your top priority, as it has the biggest impact on a diamond’s sparkle and overall appearance. Here’s how to find the best cut for your budget and ensure you’re getting the most brilliance for your investment:
A smaller, well-cut diamond will always look more dazzling than a larger diamond with a lower cut grade. If you’re working within a budget, consider choosing an Excellent or Very Good cut in a slightly lower carat weight rather than sacrificing cut quality for size.
A well-cut diamond should have:
For round brilliant diamonds, look for:
These ideal proportions help maximize light return and prevent a diamond from looking too shallow or too deep.
Fancy shapes (e.g., oval, pear, cushion, emerald cut) don’t receive official cut grades, so pay attention to facet symmetry, depth, and proportions to ensure they reflect light beautifully. If unsure, compare multiple stones under different lighting to see how they perform.
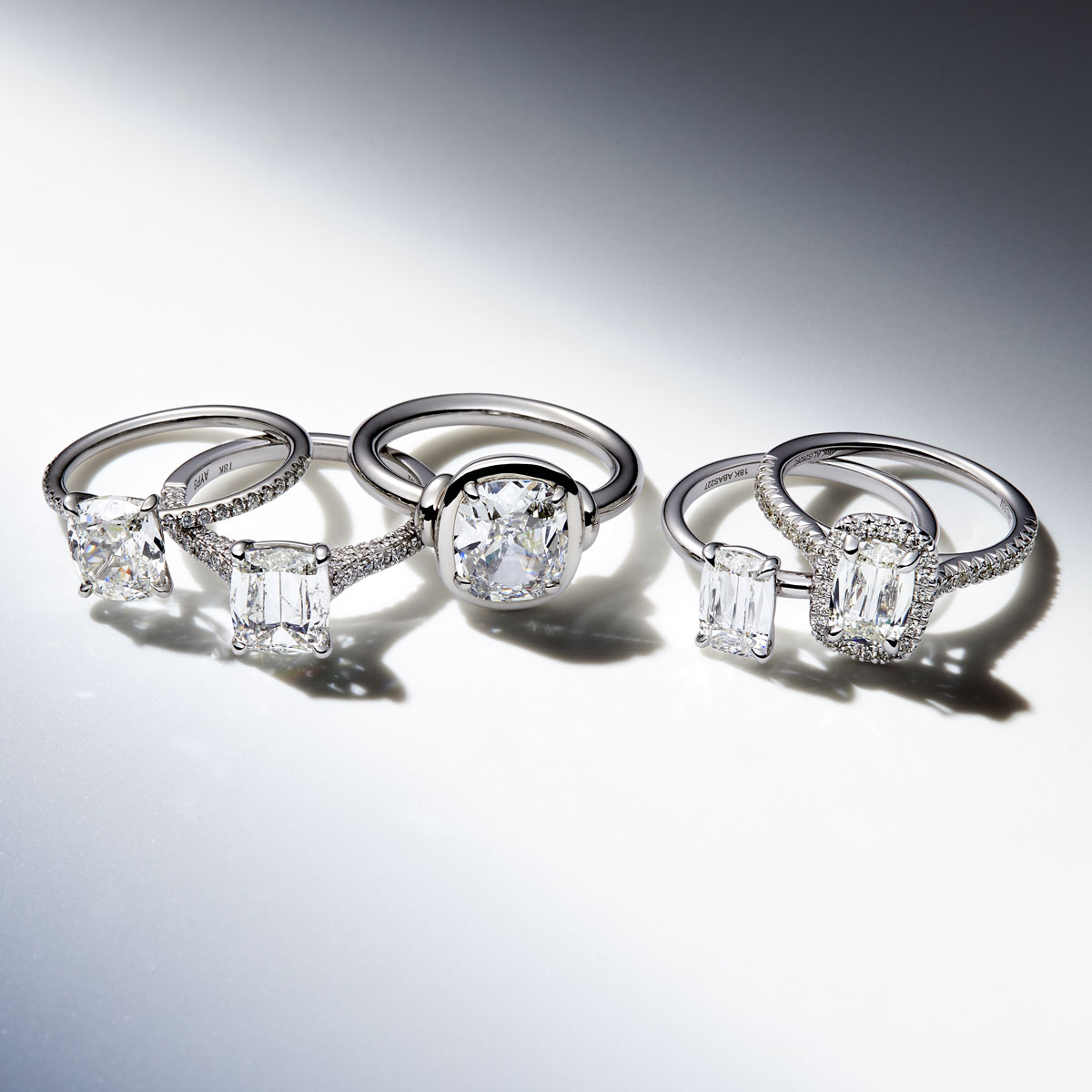



Though often confused, diamond cut grade and diamond shape refer to different aspects of a diamond’s appearance. Cut grade measures how well a diamond’s facets are proportioned to reflect light, affecting brilliance, fire, and scintillation. The GIA Cut Grade Scale (Excellent to Poor) applies only to round brilliant diamonds, while fancy shapes are assessed by proportions, symmetry, and polish.
Diamond shape refers to a diamond’s outline, such as round, oval, princess, or emerald. While cut quality determines a diamond’s sparkle, shape influences its style and perceived size. Prioritizing cut grade ensures maximum brilliance, regardless of shape.
By prioritizing cut quality and knowing what to look for, you can confidently choose a diamond that offers stunning brilliance and long-lasting beauty—regardless of size or shape.